Biopolymers
Home > Biopolymers
What are biopolymers?
Biopolymers are large molecules made up of repeating subunits that occur naturally in living organisms. Unlike synthetic polymers derived from petroleum-based sources, biopolymers are typically derived from renewable biomass, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms. These biomolecules can be composed of various building blocks, including sugars, amino acids, nucleotides, and fatty acids, depending on their biological origin and structural composition.
Common examples of biopolymers include polysaccharides like cellulose, starch, and chitin, which are abundant in plants, algae, and crustaceans. Proteins such as collagen, keratin, and silk fibroin are also biopolymers found in animals, contributing to structural tissues and fibers.
Additionally, nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are biopolymers essential for genetic information storage and protein synthesis in living organisms.
Biopolymers exhibit a wide range of properties and functionalities, making them versatile materials with applications in various industries. They are biodegradable, environmentally friendly, and can be tailored for specific uses, including slurry dewatering, turbidity control in water, agricultural products, and other water treatment solutions. Due to their renewable nature and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional plastics and polymers, biopolymers play a crucial role in advancing sustainable and eco-friendly technologies across different sectors.
Biopolymers for Water Treatment
Biopolymers play a significant role in water treatment applications across various industries, offering sustainable and effective solutions for addressing water quality challenges. In stormwater management, biopolymers are utilized for erosion control, sediment stabilization, and flocculation of suspended particles. Biopolymer-based erosion control products create a protective barrier on soil surfaces, reducing erosion rates and preventing sediment runoff into waterways during rainfall events.
In construction and civil engineering projects, biopolymers are used for soil stabilization, dewatering, and treating turbid water from excavation sites. Biopolymer additives improve soil structure, enhance water retention, and aid in sediment settling, contributing to efficient construction practices and minimizing environmental impacts related to sediment discharge.
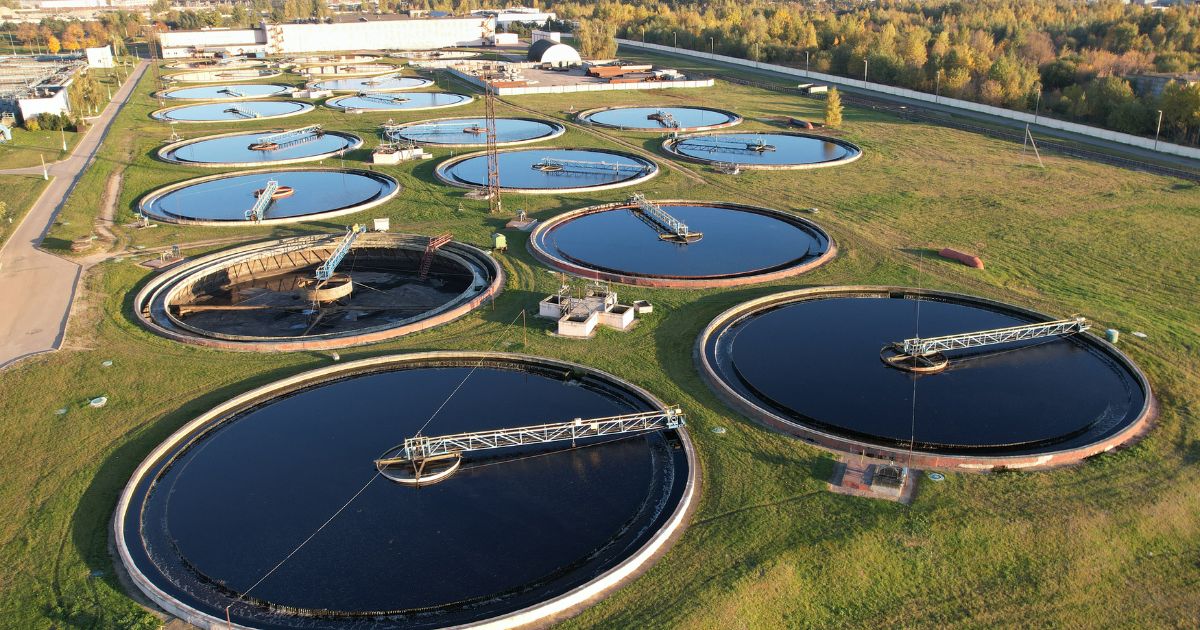

In industrial water treatment, biopolymers serve as flocculants and coagulants for removing suspended solids, colloidal particles, and organic contaminants from wastewater streams. Biopolymer-based treatment processes improve water clarity, reduce sludge volume, and enhance the efficiency of filtration and separation techniques, leading to cost-effective and environmentally friendly water purification.
Furthermore, biopolymers are employed in natural water bodies management for algae control, nutrient remediation, and aquatic habitat restoration. Biopolymer formulations targeted at controlling algal blooms bind phosphorus and other nutrients, limiting algal growth and improving water quality parameters in lakes, ponds, and reservoirs.
Overall, the versatile applications of biopolymers in water treatment underscore their importance in promoting sustainable water management practices, reducing environmental impacts, and ensuring clean and safe water resources across industries and ecosystems.




Biopolymers for Agriculture
Biopolymers offer several benefits and applications in agriculture, contributing to sustainable practices and enhanced crop productivity. Here are some ways biopolymers can help in agriculture:
- Soil Erosion Control
- Soil Amendment
- Seed Coatings
- Mulching Films
- Fertilizer Encapsulation
- Crop Protection
- Soil Bioremediation
In general, the use of biopolymers in agriculture promotes environmental sustainability, reduces reliance on synthetic chemicals, improves soil health, and enhances crop resilience, making them valuable tools for modern farming practices.
Soil Erosion Control
Biopolymers, such as those derived from natural sources like starch or cellulose, can be used in erosion control products. These biodegradable materials help stabilize soil particles, reduce erosion rates, and prevent sediment runoff, especially in sloping or vulnerable areas.
Soil Amendment
Biopolymers like bio-based hydrogels can improve soil structure and water retention capacity. When added to soil, these hydrogels absorb and retain water, releasing it slowly to plant roots, thereby reducing irrigation needs and improving drought resistance.
Seed Coatings
Biopolymers can be used to create seed coatings that enhance germination, protect seeds from pathogens, and provide nutrients for early seedling growth. These coatings improve seed viability, uniformity, and overall crop establishment.
Mulching Films
Biodegradable biopolymers can replace traditional plastic mulch films used in agriculture. These films help conserve soil moisture, control weeds, and regulate soil temperature while decomposing naturally, reducing plastic waste and environmental pollution.
Crop Protection
Biopolymers can be formulated into biopesticides or biostimulants that promote plant growth and protect crops from pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. These eco-friendly formulations offer alternatives to synthetic chemicals, supporting sustainable pest management practices.
Encapsulation
Biopolymers can be used to encapsulate fertilizers, pesticides, and nutrients, creating slow-release formulations. This controlled-release mechanism improves nutrient efficiency, reduces leaching, and minimizes environmental impact.
Soil Bioremediation
Biopolymers play a role in soil bioremediation by enhancing microbial activity and pollutant degradation. Biopolymer-based amendments can stimulate beneficial microbial populations that break down organic pollutants and improve soil health.
FAQs
Ask A Question
Do you have a question or are you looking for resources related to sustainable technologies for agriculture, water treatment, and ecosystem restoration? Reach out below!

